Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body regulates blood sugar. When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, or your cells resist the effects of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps your body use glucose, a type of sugar, for energy. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage your nerves and organs, leading to serious health complications.
The good news is that many people with diabetes can manage their condition effectively with a healthy lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and medication. The key is to recognize the early signs of diabetes and get diagnosed early.
This blog post will explore the common diabetes symptoms, with a specific focus on signs of diabetes in women and signs of diabetes in men. We’ll also discuss the importance of early detection and how to manage diabetes through a diabetic diet and continuous glucose monitoring.
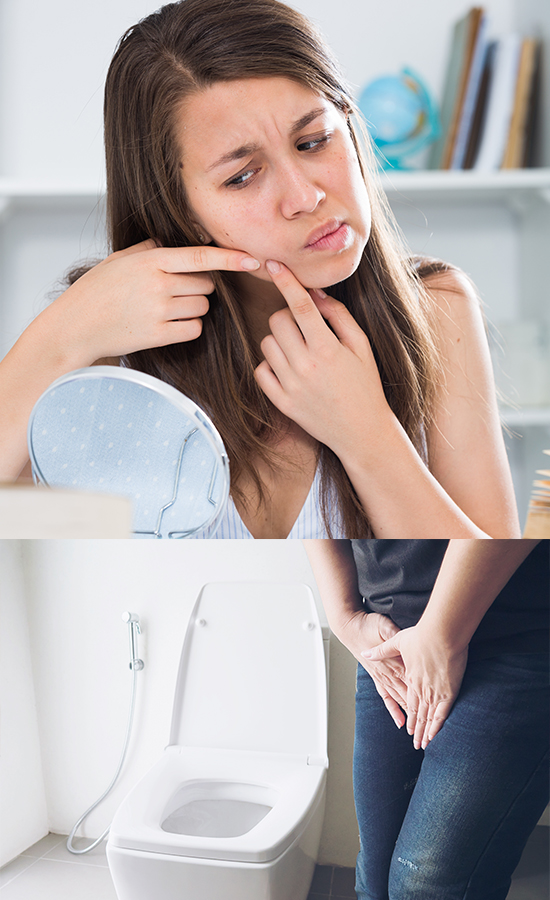

Early Warning Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore
Many people with diabetes, especially in the early stages, don’t experience any noticeable symptoms. However, there are several early signs of diabetes to watch for. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see your doctor for a diagnosis.
Here are some of the most common diabetes symptoms:
- Frequent urination: When your blood sugar levels are high, your kidneys work overtime to remove excess sugar from your blood. This can lead to frequent urination, especially at night.
- Increased thirst and hunger: When your body doesn’t have enough insulin to use glucose for energy, it tries to compensate by breaking down muscle and fat tissue. This can cause increased thirst and hunger.
- Unexplained weight loss: Although some people with diabetes may gain weight, unexplained weight loss can also be a symptom. This is because your body is breaking down muscle and fat tissue for energy.
- Blurry vision: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in your eyes, leading to blurry vision.
- Slow-healing sores: Diabetes can reduce blood flow and impair the body’s ability to heal wounds. This can lead to slow-healing sores, cuts, and infections.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can interfere with your body’s ability to use energy from food, leading to fatigue.
- Frequent infections: Diabetes can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections, such as skin infections, vaginal infections, and bladder infections.
- Skin problems: Diabetes can cause dry, itchy skin. You may also notice patches of darker skin in the armpits, groin, and neck.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.

Considering Gender Differences in Early Signs of Diabetes
While the core diabetes symptoms are similar for both men and women, there can be some subtle differences in how the condition manifests. Here’s a closer look at the signs of diabetes in women and signs of diabetes in men:

Signs of Diabetes in Women
In addition to the general diabetes symptoms, women with diabetes may also experience:
- Vaginal yeast infections: These are more common in women with diabetes due to changes in vaginal flora.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): As mentioned earlier, diabetes can increase your susceptibility to infections.
- Changes in menstrual cycle: Diabetes can affect hormone levels, leading to irregular periods or even amenorrhea (absence of periods).
- Gestational diabetes: This type of diabetes develops during pregnancy and can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Signs of Diabetes in Men
Men with diabetes may experience some of the following symptoms in addition to the general ones:
- Erectile dysfunction (ED): Diabetes can damage nerves and blood vessels, leading to ED.
- Low testosterone levels: Diabetes can affect testosterone production, leading to symptoms like decreased libido and fatigue.
- Loss of muscle mass: As mentioned earlier, the body may break down muscle tissue for energy in uncontrolled diabetes, leading to muscle loss.

Importance of Early Detection and Management
Early diagnosis and management of diabetes are crucial to prevent serious health complications, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
If you experience any of the early signs of diabetes, it’s important to see your doctor for a diagnosis. There are several tests available to diagnose diabetes, including a fasting blood sugar test, an A1C test, and an oral glucose tolerance test.
Once you’ve been diagnosed with diabetes, your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan. This plan may include:
… (continuing from previous section)
- Diet: A diabetic diet focuses on controlling blood sugar levels through healthy eating choices. This may involve limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats while incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps your body use insulin more effectively and lowers blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Medication: Depending on the severity of your diabetes, your doctor may prescribe medication, such as insulin or oral medications, to help control your blood sugar levels.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): This technology can be a valuable tool for managing diabetes. A CGM sensor is inserted under the skin and continuously measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid (fluid between cells). The sensor transmits this data to a receiver or smartphone app, allowing you to see your glucose levels in real-time and make adjustments to your diet, exercise, or medication as needed.
By following your doctor’s treatment plan and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can manage your diabetes and live a long, healthy life.

Living Well with Diabetes
Remember, diabetes doesn’t have to define you. With proper management and support, you can live a full and active life. Here are some additional tips for living well with diabetes:
- Educate yourself about diabetes: Learning as much as you can about diabetes will empower you to manage your condition effectively. Talk to your doctor, take diabetes education classes, and join a support group for people with diabetes.
- Manage stress: Stress can raise blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Get regular checkups: It’s important to see your doctor regularly for checkups and screenings to monitor your blood sugar levels and check for potential complications.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help: If you’re struggling to manage your diabetes, don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor, a diabetes educator, or a registered dietitian for support.
Medixnest
Unlock a healthier you with expert-curated blogs, latest health news, and insights from professionals. Join Medixnest’s empowering community for accurate and accessible health information.




“Hello there! I recently noticed that you’ve taken the time to visit my website, and I wanted to express my heartfelt gratitude for your interest. Your support means a lot to me. In return, I would like to extend my support by visiting your website as well.